1.4 Crack sensitive steel types of quenching cracks
Certain high-grade seamless steel pipes have a high content of alloying elements and high strength of the pipe body, so the strength factor of the stress field is relatively high. They are steel types that are sensitive to cracks. The surface or internal micro defects of pipes are prone to expand under the action of stress, forming cracks. The morphology and structure of quenching cracks on surfaces of S135 steel grade alloy structural pipes are shown in Figures 9 to 10. The occurrence probability of quenching cracks of this type of seamless steel pipe is significantly higher than that of other steel types. Because this steel type has more Cr and Mo alloy elements, high pipe strength, poor plastic deformation of the pipe microstructure, deformation storage energy can only be released by forming new surface cracks. It belongs to pipes that have a high risk of quenching cracks.
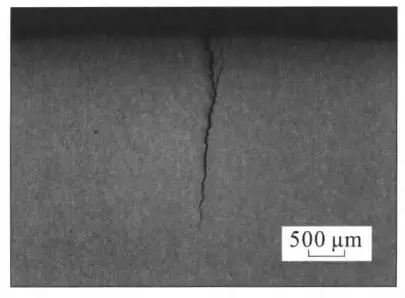
Figure 9 The morphology of quenching cracks on surfaces of S135 steel-grade alloy structural pipes
2. Preventive measures
Quenching crack is a kind of defect caused by stress cracking. It is caused when the internal stress of the material exceeds the fracture strength. Its reasons are very complicated. The internal stress is formed in the quenching process and has tensile stress properties. The internal cause of quenching cracks is the excessive stress of the material during the martensitic transformation in the quenching process, which is closely related to the chemical composition of the steel, mainly the C content and the alloying element content. Generally, the higher the C content is, the easier it is to produce cracks. It is generally believed that no quenching cracks will occur when the C content is smaller than 0.2%. At the same time, external factors such as cooling methods of quenching and surface quality of steel pipes may also cause quenching cracks.

Figure 10 The microstructure morphology of quenching cracks on surfaces of S135 steel grade alloy structural pipes
According to a variety of factors that may cause quenching cracks, the following preventive measures can be taken:
(1) Preventive measures for quenching cracks caused by surface defects
For quenching cracks caused by local stress concentration due to surface defects, it is necessary to improve the surface quality of the rolled pipe body and reduce the mutations of macroscopic defects and shapes of materials.
(2) Preventive measures for stress cracking type quenching cracks
Reducing the cooling rate can reduce the residual stress to a certain extent, that is, reduce the structural stress generated by the martensitic transformation, and the inner and outer wall phase transformation processes are carried out in a gradient. Under the premise of ensuring that the cooling rate (50 to 60℃/s) of all martensite structures is obtained, the cooling water flow should be appropriately reduced, and the internal spray plus delayed external cooling method should be adopted. Theoretically, the delay time of external spray cooling being relative to that of the internal spray cooling is the time required for the martensitic transformation of the inner wall of the steel pipe from beginning to the end, which makes the circumference of the pipe produce compressive stress. When the residual compressive stress is generated in the circumferential direction of the pipe body, quenching cracks can be greatly reduced or eliminated.
(3) Preventive measures for surface carburized quenching cracks
Measures for surface carburized quenching cracks are as the following: Properly increase the viscosity of the casting powder; reduce the slag consumption; prevent the fluctuation of the steel liquid; at the same time, because of the increase of the slag viscosity, the diffusion speed of the carbon in the molten slag layer to the molten steel will be greatly slowed down.
Adding an appropriate amount of oxidant such as MnO2 to the casting powder can promote the oxidation of carbon in the casting powder and effectively inhibit the carbon content in the enriched carbon layer and molten slag layer, or use carbon-free casting powder.
(4) Preventive measures for quenching cracks caused by steel types being sensitive to cracks
Properly adjust the steel composition; reduce the content of C element; refine the grains and improve the crack propagation resistance. The mass fractions of C and Mn should be strictly controlled for water quenching steel grades. When w(C) plus w(Mn)/3 is equal to or higher than 0.9%, there is a risk of cracking for the water quenching, and the oil quenching process should be adopted. For steel grades containing high C and Mn content, reducing the quenching temperature and cooling rate will help prevent quenching cracks in the steel pipe.
3. Conclusion
Through macroscopic and microscopic analysis as well as experimental research on the quenching cracks on the sampled pipe, the type and cause of quenching cracks are determined, and the following improvement measures are proposed:
(1) The surface defects of the pipe body caused by the rolling process are prone to stress concentration after quenching, which becomes the cause of quenching cracks. Therefore, optimize the rolling process parameters to improve the surface quality of the pipe and reduce the macroscopic defects and shape mutations of the material.
 (2) Unreasonable quenching cooling methods will lead to great residual tensile stresses in the pipe body and increase the risk of quenching cracks. Residual compressive stress will generate after the pipe body is quenched by adjusting the sequences of internal spraying and external spraying and flow rates of cooling water of the pipe body, which is an effective measure to reduce the residual stress and eliminate quenching cracks.
(2) Unreasonable quenching cooling methods will lead to great residual tensile stresses in the pipe body and increase the risk of quenching cracks. Residual compressive stress will generate after the pipe body is quenched by adjusting the sequences of internal spraying and external spraying and flow rates of cooling water of the pipe body, which is an effective measure to reduce the residual stress and eliminate quenching cracks.
(3)The molten steel is not stable in the crystallizer. The carbon-rich layer formed by casting powder in the melting process contacting the molten steel and causing recarburization of casting blank is one of the reasons for the carbon increase of the casting blank. Adopt carbon free casting powder and control such as drawing speeds, vibration frequency of the crystallizer to prevent fluctuations of steel liquids and maintain a stable thickness of the liquid slag layer.
(4) Properly adjust the steel's composition that is sensitive to cracks, and reasonably select the cooling medium and cooling rate according to the mass fractions of C and Mn. 


 (2) Unreasonable quenching cooling methods will lead to great residual tensile stresses in the pipe body and increase the risk of quenching cracks. Residual compressive stress will generate after the pipe body is quenched by adjusting the sequences of internal spraying and external spraying and flow rates of cooling water of the pipe body, which is an effective measure to reduce the residual stress and eliminate quenching cracks.
(2) Unreasonable quenching cooling methods will lead to great residual tensile stresses in the pipe body and increase the risk of quenching cracks. Residual compressive stress will generate after the pipe body is quenched by adjusting the sequences of internal spraying and external spraying and flow rates of cooling water of the pipe body, which is an effective measure to reduce the residual stress and eliminate quenching cracks.